Curious about how air source heat pump systems work and what benefits they offer?
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about these innovative heating systems. From understanding the components of an air source heat pump system to the different types available, we will cover it all.
Discover the energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental benefits of using an air source heat pump system, as well as the important factors to consider before installation.
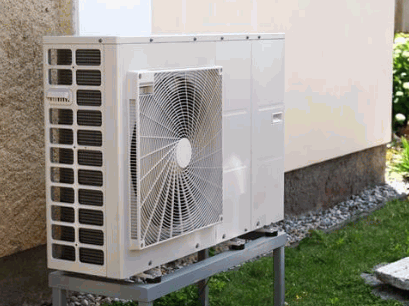
What Is An Air Source Heat Pump System?
An air source heat pump (ASHP) is an efficient energy system that provides heating and cooling for buildings by transferring heat between the inside and outside environments, making it a sustainable solution for maintaining optimal indoor temperatures.
Explore: How Long Does It Take To Install A Ground Source Heat Pump

How Does An Air Source Heat Pump System Work?
An air source heat pump system works by transferring heat from the outside air to the inside of a building using a cycle involving refrigerants, coils, and a compressor.
During the operational process of an air source heat pump system, the refrigerant starts its journey in the evaporator coil. Here, it absorbs heat from the outdoor air, turning it into a low-pressure gas. This gas is then compressed by the compressor, increasing its temperature and pressure before entering the condenser coil.
The key principle of heat exchange comes into play as the hot refrigerant releases its heat to the indoor air, causing it to condense back into a liquid state. The cycle repeats as the liquid refrigerant flows back to the evaporator to absorb more heat from the surroundings.

What Are The Components Of An Air Source Heat Pump System?
The main components of an air source heat pump system include the outdoor unit, indoor unit, refrigerant, and compressor, each playing a crucial role in the system's operation.
Outdoor Unit
The outdoor unit of a heat pump houses the heat exchanger, which absorbs heat from the outside air.
The heat exchanger is a crucial part of the outdoor unit as it allows the heat pump system to extract heat energy from the ambient air, even in cooler temperatures. This component is typically made of coils or fins that facilitate the transfer of heat. As the refrigerant circulates through the coils, it absorbs the heat from the air outside, which is then carried into the indoor unit for distribution.
The outdoor unit also contains a fan that helps in the process of drawing air over the heat exchanger for efficient heat transfer.

Indoor Unit
The indoor unit of an air source heat pump is responsible for distributing the heated or cooled air within the building.
During the heating mode, the indoor unit draws in outdoor air, which is then transferred through the evaporator coil. The refrigerant within the coil absorbs heat from the air, transforming it into warm air.
On the other hand, in cooling mode, the indoor unit takes in warm indoor air, which passes through the evaporator coil. The refrigerant in the coil absorbs the heat, resulting in cool air being circulated back into the room.

Refrigerant
The refrigerant in an air source heat pump plays a vital role in the vapor-compression refrigeration process, absorbing and releasing heat to facilitate temperature regulation.
Refrigerants are crucial for heat pumps as they have properties that enable them to transition between liquid and gas states efficiently. When the refrigerant is in a gaseous state, it absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it down. This heated gas is then compressed by the compressor, raising its temperature.
- The hot, compressed gas flows through the condenser coils, where it releases heat to the outside environment, causing it to condense into a high-pressure liquid.
- This high-pressure liquid then moves through the expansion valve, which lowers its pressure, allowing it to evaporate and absorb heat again, continuing the cycle.
This constant flow of the refrigerant through the system is what enables the heat pump to regulate indoor temperatures effectively.
Compressor
The compressor in an air source heat pump compresses the refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure to enable efficient heat transfer.
This crucial component of the heat pump plays a key role in the refrigeration cycle. By compressing the refrigerant gas, it causes the molecules to move closer together, increasing their energy and temperature. This high-pressure, high-temperature gas then flows to the condenser, where it releases heat to the outside air. The compressor's function is essential for the heat pump to extract heat from the outside air and transfer it into the indoor space. Its efficiency directly impacts the overall performance of the system, affecting both heating capacity and energy consumption. A well-functioning compressor is vital to ensure the heat pump operates effectively and economically.
What Are The Types Of Air Source Heat Pump Systems?
There are several types of air source heat pump systems, including air-to-air heat pumps, air-to-water heat pumps, and hybrid heat pumps, each designed to meet different heating and cooling needs.
Air-To-Air Heat Pump
An air-to-air heat pump provides heating and cooling by transferring heat between indoor and outdoor air, functioning similarly to an air conditioning system.
Unlike traditional air conditioning systems that rely solely on refrigerant to cool indoor air, air-to-air heat pumps use a refrigerant cycle to transfer heat in both directions, extracting heat from the outdoor air to warm the indoors during colder months and expelling heat from indoor air to cool the space in warmer weather.
These pumps work efficiently in moderate climates, as they can extract heat from outdoor air even when temperatures are low. This makes them cost-effective and energy-efficient solutions for maintaining indoor comfort throughout the year.

Air-To-Water Heat Pump
An air-to-water heat pump transfers heat from outside air to water, providing heating for radiators, underfloor heating, and hot water systems.
These innovative systems work by absorbing heat from the ambient air using a refrigerant. The heat is then transferred to a water circuit, which can be used for space heating or to heat domestic hot water. By utilizing renewable energy sources like the air, air-to-water heat pumps offer a sustainable heating solution.
Energy efficiency is a key advantage of these pumps, as they can produce more energy than they consume, resulting in reduced utility bills. Their versatility allows them to complement various heating systems, making them suitable for different types of buildings and applications.

Hybrid Heat Pump
A hybrid heat pump combines the benefits of an air source heat pump with a traditional gas boiler, optimizing energy efficiency and performance.
One of the key advantages of hybrid heat pumps is their ability to offer significant energy savings compared to traditional heating systems. By harnessing the efficiency of an air source heat pump in moderate temperatures and seamlessly switching to a gas boiler in colder conditions, homeowners can enjoy lower energy bills throughout the year.
In addition, hybrid heat pumps excel in providing improved performance in varying temperatures. As they are designed to adapt to changing climate conditions, they are highly efficient in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment regardless of the outdoor weather.
The integration of hybrid heat pumps with existing gas boiler systems is a seamless process that allows for a smooth transition without the need for extensive modifications. This versatility makes them a popular choice for homeowners looking to upgrade their heating systems while still utilizing their current infrastructure.

What Are The Benefits Of Using An Air Source Heat Pump System?
Using an air source heat pump system offers numerous benefits, including high energy efficiency, significant cost savings, environmental friendliness, and versatility in providing both heating and cooling solutions.
Energy Efficiency
Air source heat pumps are highly energy-efficient, boasting impressive COP and efficiency ratings that make them an eco-friendly choice.
One of the key metrics used to measure the efficiency of ASHPs is the Coefficient of Performance (COP). This value signifies the ratio of heating or cooling output to the amount of electrical energy input. The higher the COP, the more efficient the heat pump is in converting electricity into heating or cooling power.
ASHPs also come with efficiency ratings, such as SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor), which indicate their performance levels during specific conditions. These ratings help consumers choose the most suitable system for their needs, ensuring optimal energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Cost Savings
The cost savings associated with air source heat pumps come from lower running costs, reduced energy bills, and minimal maintenance requirements.
Air source heat pumps are known for their high efficiency, which means they require less energy to operate compared to traditional heating systems. This increased efficiency leads to significant cost savings over time as the energy bills are consistently lower.
The reduced maintenance requirements of ASHPs contribute to long-term financial benefits. With fewer parts to upkeep and a simpler design, the maintenance costs are minimized, further adding to the overall savings.
Another factor is the lower installation expenses associated with air source heat pumps. These systems are generally easier and more cost-effective to install, resulting in reduced upfront costs and faster payback periods for homeowners or businesses investing in this technology.
Environmentally Friendly
Air source heat pumps are environmentally friendly as they reduce greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide, contributing to a cleaner environment.
By harnessing renewable energy sources such as the air outside, ASHPs offer a sustainable solution for heating and cooling buildings. This not only helps to combat climate change by reducing reliance on fossil fuels but also plays a significant role in promoting sustainability. ASHPs operate efficiently, converting ambient heat into usable energy, thereby minimizing energy wastage. As a result, they not only lower carbon footprints but also lead to cost savings for users in the long run.
Versatility
The versatility of air source heat pumps lies in their ability to provide both heating and cooling, ensuring a comfortable indoor air environment year-round.
Whether it's the scorching heat of summer or the frosty chills of winter, these systems adapt adeptly to maintain the desired temperature inside your home or office. The energy-efficient design of ASHPs not only makes them eco-friendly but also cost-effective, offering savings on utility bills in the long run.
Beyond just regulating temperature, air source heat pumps can also help maintain optimal humidity levels, creating a healthier and more enjoyable living space for occupants.

What Are The Factors To Consider Before Installing An Air Source Heat Pump System?
Before installing an air source heat pump system, it is essential to consider various factors such as climate, the size and layout of the property, the existing heating system, and the potential costs and savings.
Climate
The local climate plays a crucial role in the performance of an air source heat pump, especially in colder temperatures where efficiency might be affected.
When temperatures drop, the effectiveness of an air source heat pump can diminish, requiring the system to work harder to extract heat from the air. In extreme cold conditions, the pump may struggle to maintain desired indoor temperatures, leading to decreased efficiency and higher energy consumption. This underscores the importance of proper insulation and sizing of the system to ensure optimal performance.
Size And Layout Of Property
The size and layout of your property are critical considerations when installing an air source heat pump to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Properly assessing the dimensions and design of your property can greatly impact the successful installation of an ASHP. For example, a larger property may require a more powerful heat pump to adequately heat or cool the space, while a smaller property might benefit from a compact and energy-efficient unit.
The layout of your property plays a significant role in the placement of the ASHP. Strategic placement, such as ensuring adequate airflow and minimal obstructions, is crucial for the system to operate efficiently and effectively.
Existing Heating System
Evaluating your existing heating system is necessary to determine how well an air source heat pump can connect with or replace gas boilers or other setups.
Since ASHPs operate using electricity and draw heat from the outside air, they offer a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional heating methods. The integration process involves assessing the compatibility of your current system with the ASHP and making necessary adjustments. This may include upgrading insulation to improve efficiency, installing appropriate controls for optimal performance, and ensuring proper ventilation. It's crucial to consult with a professional to determine the most suitable configuration for seamless operation and maximum energy savings.
Cost And Savings
Understanding the cost and savings involved in installing an air source heat pump is vital for making an informed decision about the investment.
When considering the initial costs of an air source heat pump, it's important to account for the price of the unit itself, as well as the expenses associated with installation. Typically, the upfront investment for an air source heat pump can range from $5,000 to $10,000 or more. These costs can vary depending on factors such as the size of the unit and the complexity of installation.
Running costs of air source heat pumps mainly revolve around electricity consumption. It's crucial to factor in the increase in energy bills that may come with using a heat pump as your primary heating source. While these ongoing expenses can add up, it's essential to consider the long-term financial benefits that an air source heat pump can offer.

