Curious about ground source heat pumps?
Wondering how they work and what benefits they offer?
In this article, we'll explore the ins and outs of ground source heat pumps, including their energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental friendliness.
We'll also dive into the factors that affect installation time, common challenges, and how to choose the right installer.
If you're considering installing a ground source heat pump, keep reading to learn everything you need to know!

What Is A Ground Source Heat Pump?
A ground source heat pump is a type of heating technology that harnesses renewable energy from the ground to provide heating and hot water for homes and buildings. These systems utilize thermal energy stored in the earth to efficiently heat residential and commercial properties.
Ground source heat pumps consist of three main components:
- The ground loop, which is buried underground and contains a mixture of water and antifreeze, absorbs heat from the earth.
- The heat pump unit is where the absorbed heat is compressed and used to heat the building.
- The distribution system, which distributes the heated air or water throughout the building, provides a consistent and comfortable indoor environment.
Discover: How Efficient Are Air Source Heat Pumps In Winter
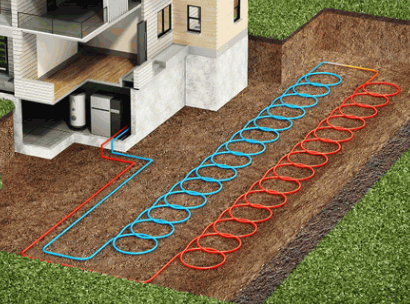
How Does A Ground Source Heat Pump Work?
A ground source heat pump works by extracting heat from the ground through a system of pipes known as a ground loop, using electricity to transfer thermal energy into the building's heating and hot water systems.
The ground loop, buried beneath the surface, circulates a mixture of water and antifreeze through the pipes. As the liquid moves through the loop, it absorbs the heat stored in the ground, which maintains a relatively constant temperature below the frost line. This heat is then transferred to the heat pump unit inside the building, where a refrigerant in the evaporator coil absorbs the heat, evaporates, and is compressed into a high-pressure gas. The heat is released into the building through a heat exchanger, providing warmth and hot water efficiently.
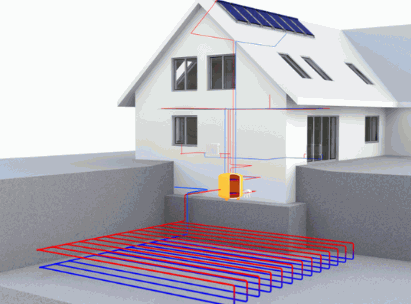
What Are The Benefits Of Installing A Ground Source Heat Pump?
Installing a ground source heat pump offers several benefits, including improved energy efficiency, significant cost savings, and a positive environmental impact by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of a ground source heat pump is its high energy efficiency, as it can convert thermal energy from the ground with a high coefficient of performance.
Ground source heat pumps achieve their high efficiency by utilizing stable underground temperatures, typically warmer than the air in cold weather and cooler in hot weather. This technology leverages the natural thermal properties of the earth to provide heating, cooling, and hot water for residential and commercial buildings. The coefficient of performance (COP) of a heat pump indicates its efficiency in converting energy input to useful heat output. A higher COP signifies better efficiency, demonstrating how effectively the pump can transfer thermal energy from the ground to the building.
Cost Savings
Ground source heat pumps offer substantial cost savings over time, with potential financial support from schemes like the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) administered by Ofgem and the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS).
Although the initial installation cost of a ground source heat pump may be higher than traditional heating systems, the long-term savings in energy bills can outweigh this expense. With advancements in technology and increased awareness of sustainable living, more homeowners are opting for these eco-friendly heating solutions.
The RHI provides financial incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable heating technologies, making the transition to a ground source heat pump even more economically viable for households. By offsetting the initial investment through reduced energy costs and government support, homeowners can enjoy both environmental benefits and financial savings in the long run.
Environmentally Friendly
Ground source heat pumps are environmentally friendly, as they utilize renewable energy, contribute to sustainability, and help in environmental protection by reducing carbon emissions.
By harnessing the stable underground temperatures, ground source heat pumps significantly reduce the reliance on fossil fuels, minimizing the release of harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This reduction in carbon emissions plays a crucial role in combating climate change and global warming. The energy efficiency of these systems means less strain on traditional energy sources, promoting a more sustainable energy landscape for future generations.

What Are The Factors That Affect Installation Time?
The time required to install a ground source heat pump can vary based on several factors, including the size of the property, the type of ground loop system, the accessibility of the property, and the experience of the installer.
Size Of The Property
The size of the property significantly impacts the installation time of a ground source heat pump, as larger properties may require more extensive ground loops and longer installation periods.
When dealing with larger properties, the ground source heat pump installation process becomes more complex. A substantial property demands an increased number of ground loops to effectively transfer heat from the ground to the heat pump. These additional loops not only require more labor and materials but also necessitate meticulous planning to ensure optimal heat exchange efficiency.
The installation time for a ground source heat pump on a larger property is also extended due to the sheer amount of ground that needs to be excavated and prepared for the installation. Technicians need to carefully map out the location for each loop, considering factors like soil composition and underground utility lines, which add to the overall complexity of the project.
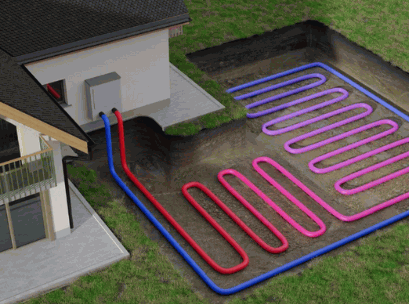
Type Of Ground Loop System
The type of ground loop system, whether horizontal or vertical (borehole), affects the installation process and duration for a ground source heat pump.
Horizontal ground loop systems involve trenches being dug horizontally in the earth just a few feet beneath the surface. This method is more common in areas with ample land space but may require longer trenches to compensate for the lower depth. In contrast, vertical ground loop systems, also known as borehole systems, dig deep holes into the ground, requiring less land area but more labor due to the depth. Typically, horizontal systems are easier to install and less expensive, but vertical systems are more efficient in areas with limited space.
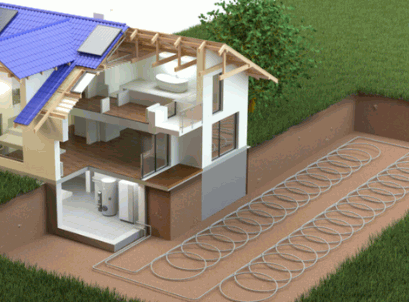
Accessibility Of The Property
The accessibility of the property can also influence the installation time, as difficult-to-reach areas may require specialized equipment and additional labor.
For properties with limited access, challenges may arise in transporting heavy machinery or materials to the designated installation site. Coordination between the installation team and property owners becomes crucial to plan logistics effectively. Navigating through narrow pathways or staircases can pose obstacles that demand creative solutions, such as using smaller equipment or implementing alternative routes.
Experience Of The Installer
The experience and qualifications of the installer, such as certification under the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS), play a crucial role in determining the efficiency and speed of the installation process.
Experienced and certified installers bring a level of expertise that can significantly impact the overall installation timeline. Their deep understanding of the technical requirements, safety protocols, and best practices ensures that the installation is carried out seamlessly and efficiently.
- Installer proficiency also minimizes the chances of errors or setbacks during the installation, ultimately saving time and avoiding costly delays.
How Long Does It Typically Take To Install A Ground Source Heat Pump?
The typical installation time for a ground source heat pump varies depending on the type of property, with residential installations often taking between one to two weeks and commercial installations potentially requiring a longer timeframe due to increased complexity and scale.
Residential Properties
For residential properties, the installation of a ground source heat pump typically takes around one to two weeks, depending on factors such as property size and ground conditions.
The installation process begins with a comprehensive assessment of the property to determine the best location for the heat pump unit and the ground loop. The preparation involves excavation for the ground loop, which is typically buried several feet underground. Once the trench is dug, the ground loop, consisting of a series of pipes, is installed and connected to the heat pump unit. This loop serves as the conduit for transferring heat between the earth and the heat pump. After the ground loop installation, the system is thoroughly tested to ensure proper functionality and efficiency.
Commercial Properties
Installing a ground source heat pump in commercial properties can take longer due to the larger scale and more complex system requirements, often extending beyond two weeks.
One of the key challenges in installing ground source heat pumps in commercial properties is the need for significantly larger ground loops to effectively extract heat from the ground. These bigger loops require more space, careful planning, and excavation work to set them up properly. The installation of a commercial heat pump system may require special permits and compliance with building codes, adding an extra layer of complexity to the process. Proper sizing and designing of the ground loop system is crucial to ensure efficient operation and long-term cost savings for the property owner.

What Is The Process Of Installing A Ground Source Heat Pump?
The process of installing a ground source heat pump involves several key steps, starting with site assessment and design, followed by ground loop installation, the connection of pipes to the heat pump, and finally, integration with the building's heating system.
Once the site assessment is completed, the next step is to determine the appropriate size and layout of the ground loop system. This involves digging trenches or drilling boreholes to accommodate the loop configuration. The pipes are then laid out in these spaces, ensuring proper spacing and depth for efficient heat exchange.
- After the ground loop is installed, the next phase involves connecting the pipes to the heat pump unit. This step requires careful attention to detail to ensure proper sealing and insulation to prevent any heat loss.
- Once the connections are secured, the system is ready for integration with the building's existing heating system. This step involves setting up the controls, testing the system for proper functionality, and fine-tuning the settings for optimal performance.

What Are The Common Challenges Of Installing A Ground Source Heat Pump?
Installing a ground source heat pump can present several challenges, including difficult ground conditions, limited space for the ground loop system, and navigating permitting and zoning restrictions.
Difficult Ground Conditions
Difficult ground conditions, such as rocky or waterlogged soil, can complicate the installation of a ground source heat pump and require specialized equipment or techniques.
Rocky soil, for instance, may necessitate the use of rock drilling equipment to create boreholes for the heat pump system, adding complexities to the installation process. Waterlogged soil poses challenges in thermal conductivity, impacting the pump's efficiency. Therefore, site-specific assessments are essential to determine the suitable installation methods.
Limited Space For Ground Loop System
Limited space for installing the ground loop system can be a significant challenge, particularly in urban areas or properties with small yards.
For properties facing this constraint, alternative solutions can be explored to harness geothermal energy effectively. One option is to consider vertical boreholes which involve drilling deep into the ground to create a compact yet efficient geothermal loop system. This method requires less horizontal space while still maximizing heat exchange with the Earth. Utilizing innovative loop designs, such as slinky coils or directional drilling, can optimize the available space and enhance the system's performance.
Permitting And Zoning Restrictions
Permitting and zoning restrictions can delay the installation process of a ground source heat pump, requiring compliance with local regulations and sometimes affecting eligibility for incentives like the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI).
When dealing with the complex regulatory landscape surrounding ground source heat pumps, it's crucial to thoroughly understand the specific permitting requirements set forth by local authorities. Obtaining the necessary permits involves meticulous planning and coordination to ensure that the installation proceeds smoothly. Navigating zoning restrictions demands careful consideration of land use laws and building codes to guarantee compliance with all applicable regulations. By proactively addressing these challenges, homeowners can streamline the approval process and expedite the implementation of their energy-efficient heating solution.

How To Choose The Right Installer For A Ground Source Heat Pump?
Choosing the right installer for a ground source heat pump involves checking credentials and experience, asking for references and reviews, and obtaining multiple quotes to ensure a fair price and quality service.
Check Credentials And Experience
To ensure a successful installation, it's crucial to check the credentials and experience of the installer, looking for certifications such as the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS).
Verifying the qualifications of the installer is essential as it guarantees that the individual possesses the necessary skills and knowledge required to carry out the installation effectively. Having the MCS certification indicates that the installer has undergone specific training and meets industry standards in installing ground source heat pumps.
- Experience plays a vital role in ensuring a seamless installation process. An experienced installer is likely familiar with various system configurations and potential challenges that may arise, allowing them to address issues efficiently.
- By hiring a qualified and experienced installer, homeowners can have peace of mind that the installation will be done professionally, minimizing the risk of errors or complications in the future.
- It's advisable to inquire about the installer's past projects and request references to gain insight into their track record and customer satisfaction levels.
Ask For References And Reviews
Asking for references and reading reviews from previous clients can provide valuable insights into the reliability and quality of an installer.
Customer feedback acts as a window into the experience others have had with the installer, allowing you to gauge their professionalism, timeliness, and overall service quality. Evaluating reviews helps in understanding common themes or recurring issues that may raise red flags. References offer a personal touch, enabling you to directly speak with past clients to gather more in-depth information about the installer's work ethic and results.
Get Multiple Quotes
Obtaining multiple quotes from different installers, such as those found on GreenMatch, can help you compare costs and services to find the best value for your ground source heat pump installation.
Once you have requested quotes, it's essential to thoroughly review each proposal. Look beyond just the prices listed; consider the service quality offered by each installer. Check for reviews or references to gauge customer satisfaction.
Pay close attention to the warranty terms provided by the installers. A comprehensive warranty can save you money in case of future repairs or malfunctions.
Creating a comparison table can be helpful; list out the costs, services, warranties, and any additional benefits offered by each installer.
